assess for meniscus tear with which test|diagnose meniscus tear without mri : bulk McMurray test (meniscus cartilage tear): Lateral meniscus tear: With patient supine, fully flex the knee, place forefingers on lateral side of joint line, then with applying valgus stress and internal rotation of leg, extend the knee looking for both pop/click and pain. Replacement Small Tray for Midmark / Ritter M7 Autoclave Sterilizer. Replaces OEM #002-0.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Although disc diffusion showed robustness to test cefiderocol susceptibility, large areas of technical uncertainty (ATU) are reported by current EUCAST breakpoints.
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to .The McMurray test is a quick first step your provider can use to determine if anything in your knee is damaged. You’ll probably still need other tests like an MRI to confirm that your meniscus is torn. Talk to your provider about which other tests and treatments you’ll need.
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates .The McMurray test is used to assess the integrity of the medial and lateral meniscus, specifically testing for meniscal tears, which is the most common injury to the knee. The McMurray test is commonly used along with the joint line tenderness test to identify meniscal injury.McMurray test (meniscus cartilage tear): Lateral meniscus tear: With patient supine, fully flex the knee, place forefingers on lateral side of joint line, then with applying valgus stress and internal rotation of leg, extend the knee looking for both pop/click and pain.
Diagnostic accuracy of the Thessaly test, standardised clinical history and other clinical examination tests (Apley’s, McMurray’s and joint line tenderness) for meniscal tears in comparison with magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis.Provocative maneuvers that may elicit characteristic results in the presence of a meniscal tear include the following: Apley test – Pain at the medial or lateral joint McMurrays test – Pain or a reproducible click; Special Test: McMurray’s Test PURPOSE: Testing for Injury to the MenisciOne of the main tests for meniscus tears is the McMurray test. Your doctor will bend your knee, then straighten and rotate it. This puts tension on a torn meniscus. If you have a meniscus tear, this movement may cause pain, clicking, or a clunking sensation within the joint. Meniscal injuries can occur in isolation or in association with collateral or cruciate ligament tears. (See "Medial (tibial) collateral ligament injury of the knee" and "Anterior cruciate ligament injury".) The diagnosis and treatment of meniscal injuries will be reviewed here.
McMurray’s test is used to assess the menisci for evidence of a meniscal tear. This test is not usually expected in an OSCE scenario as it can cause significant pain and even meniscal injury if performed incorrectly. It is important however to have an awareness of how and why the test is performed. McMurray’s test for assessing the medial . A torn meniscus often can be identified during a physical exam. Your doctor might move your knee and leg into different positions, watch you walk, and ask you to squat to help pinpoint the cause of your signs and symptoms.
The McMurray test is a quick first step your provider can use to determine if anything in your knee is damaged. You’ll probably still need other tests like an MRI to confirm that your meniscus is torn. Talk to your provider about which other tests and treatments you’ll need.McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates .The McMurray test is used to assess the integrity of the medial and lateral meniscus, specifically testing for meniscal tears, which is the most common injury to the knee. The McMurray test is commonly used along with the joint line tenderness test to identify meniscal injury.
McMurray test (meniscus cartilage tear): Lateral meniscus tear: With patient supine, fully flex the knee, place forefingers on lateral side of joint line, then with applying valgus stress and internal rotation of leg, extend the knee looking for both pop/click and pain.Diagnostic accuracy of the Thessaly test, standardised clinical history and other clinical examination tests (Apley’s, McMurray’s and joint line tenderness) for meniscal tears in comparison with magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis.
Provocative maneuvers that may elicit characteristic results in the presence of a meniscal tear include the following: Apley test – Pain at the medial or lateral joint McMurrays test – Pain or a reproducible click; Special Test: McMurray’s Test PURPOSE: Testing for Injury to the MenisciOne of the main tests for meniscus tears is the McMurray test. Your doctor will bend your knee, then straighten and rotate it. This puts tension on a torn meniscus. If you have a meniscus tear, this movement may cause pain, clicking, or a clunking sensation within the joint. Meniscal injuries can occur in isolation or in association with collateral or cruciate ligament tears. (See "Medial (tibial) collateral ligament injury of the knee" and "Anterior cruciate ligament injury".) The diagnosis and treatment of meniscal injuries will be reviewed here.
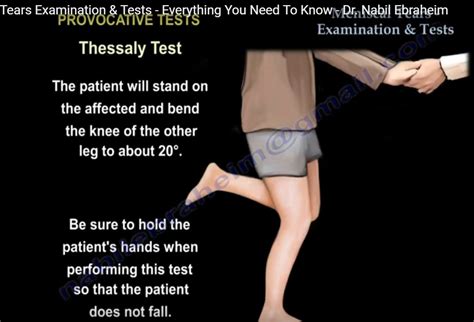
standing test for meniscus tear
McMurray’s test is used to assess the menisci for evidence of a meniscal tear. This test is not usually expected in an OSCE scenario as it can cause significant pain and even meniscal injury if performed incorrectly. It is important however to have an awareness of how and why the test is performed. McMurray’s test for assessing the medial .
pusher centrifuge
special test for meniscus tear

positive test for meniscus tear
In the modern type of autoclave, steam circulates within the jacket and is supplied under high pressure to the closed inner chamber where goods are kept for sterilization. One-fifth part of the cylinder is filled with .This chart summarizes the different ISO types of chemical indicators. It also provides examples of applications and STERIS Life Sciences products available for each type. Use it to help choose the correct chemical indicator for monitoring specific sterilization processes.
assess for meniscus tear with which test|diagnose meniscus tear without mri